What is UML
The Unified Modeling Language (UML), is a standardized modeling language consisting of an integrated set of diagrams, developed to help system and software developers for specifying, visualizing, constructing, and documenting the artifacts of software systems, as well as for business modeling and other non-software systems.
The UML represents a collection of best engineering practices that have proven successful in the modeling of large and complex systems. The UML uses mostly graphical notations to express the design of software projects. Using the UML helps project teams communicate, explore potential designs, and validate the architectural design of the software. In this Chapter, we will give you detailed ideas about what is UML, the history of UML and a description of each UML diagram type, along with UML examples.

The Origin of UML
The goal of UML is to provide a standard notation that can be used by all object-oriented methods and to select and integrate the best elements of precursor notations. UML has been designed for a broad range of applications. Hence, it provides constructs for a broad range of systems and activities (e.g. distributed systems, analysis, system design and deployment).
In 1994, Jim Rumbaugh, the creator of OMT, stunned the software world when he left General Electric and joined Grady Booch at Rational Corp. The aim of the partnership was to merge their ideas into a single, unified method (the working title for the method was indeed the "Unified Method").
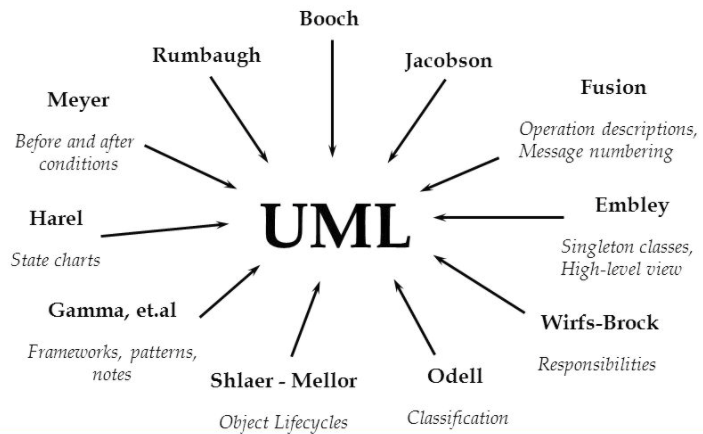
By 1995, the creator of OOSE, Ivar Jacobson, had also joined Rational, and his ideas (particularly the concept of "Use Cases") were fed into the new Unified Method - now called the Unified Modelling Language1. UML is a notation that resulted from the unification from:
- Was developed by Grady Booch, Ivar Jacobson and James Rumbaugh, known as the 3 Amigos, at Rational Software in 1990s
- Adopted by Object Management Group (OMG) in 1997
- Accepted by International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in 2000
- The current vesrion of UML is 2.4.1 – published in 2011
UML has also been influenced by other object-oriented notations:
- Mellor and Shlaer [1998]
- Coad and Yourdon [1995]
- Wirfs-Brock [1990]
- Martin and Odell [1992]
UML also includes new concepts that were not present in other major methods at the time, such as extension mechanisms and a constraint language. UML also includes new concepts that were not present in other major methods at the time, such as extension mechanisms and a constraint language.
Learning More about UML